Project Background
A company specializes in the research and development and manufacturing of ultra-thin micro-projection optical engines and laser projection display products. As the core component of projection products, the integration and operating power of imaging display chips are constantly increasing. Researchers face a key challenge: will the heat generated by the chip during operation affect the color, brightness, and stability of the final projected image?
User Pain Points
➤ The small size of microchips makes temperature measurement difficult
Microchips are extremely small, and their critical heat-generating areas are even smaller. Accurately capturing the overall heat distribution and real-time temperature data of the chip is quite challenging.
➤ R&D lacks comprehensive data support
It is necessary to understand the complete temperature field distribution and temperature data of the entire chip surface and even the surrounding minute areas to assist in the scientific and comprehensive assessment of thermal risks.
➤ The R&D testing process requires minimal or no interference
The R&D testing needs to simulate the dynamic working state of the chip under different power levels. The goal is to synchronously and continuously record temperature changes and real-time projection imaging effects without interfering with or with minimal interference to the chip's operation, and to establish a "temperature-image" correlation curve.
Solutions
A highly realistic simulation environment was set up at the test site : a working temperature scenario of 80~150℃ was constructed using a microcomputer heating platform to conduct heating tests.
The company used the Guide H6S series intelligent thermal camera (with a dedicated macro lens) to conduct comparative tests with traditional contact thermometers. The tests captured the heat changes of the projection chip under different power conditions, and helped to evaluate whether temperature fluctuations would affect the imaging display effect. This provided core data support for optimizing the product's optical performance and improving its operational stability.

Experimental results demonstrate that the Hammer series intelligent thermal camera has outstanding core advantages:
Its dedicated macro lens allows for close-up observation at a distance of 100mm, visually presenting the heating status and temperature information of the ultra-thin micro-projection chip.
Compared to contact thermometers, the H6S uses non-contact detection , enabling accurate temperature measurement from a distance without touching the chip being tested. This avoids interference with the chip's operating status and allows for real-time capture of the chip's dynamic heat generation changes at different power levels .
Based on simultaneous testing using the two tools, the team not only precisely quantified the chip's heat generation patterns and temperature field distribution under operating conditions , but also obtained reliable evidence to assess the impact of temperature on imaging performance .
Project Value
➤ Capturing Microchip Thermal Data, Solving Temperature Measurement Challenges
The Hammer series, equipped with a dedicated macro lens, overcomes the bottleneck of micro-target temperature measurement, achieving precise detection of small targets at the 50μm level. It fully presents the chip's thermal distribution, providing core data for imaging stability analysis.
➤ Non-Intrusive Detection, Ensuring Data Reliability
The non-contact measurement method avoids physical interference with the chip caused by contact temperature measurement, accurately reproducing the chip's heating state in real-world operating environments, making the detection results more valuable.
➤ Accelerating R&D Iteration, Reducing Trial and Error Costs
Based on the "temperature-imaging display" linkage, it assists in evaluating the impact of temperature on imaging, optimizing the optical system layout and heat dissipation design, and significantly shortening the R&D cycle.
➤ Establishing Data -Driven Quality Control Standards
Integrating infrared thermal imaging detection into the R&D and quality control processes, using objective temperature data as the core, it constructs a standard for verifying the thermal performance of projection chips, ensuring the stability of mass-produced products.
In the field of precision electronics manufacturing, components and chips are constantly evolving towards miniaturization , which places more stringent requirements on the accuracy of thermal management testing.
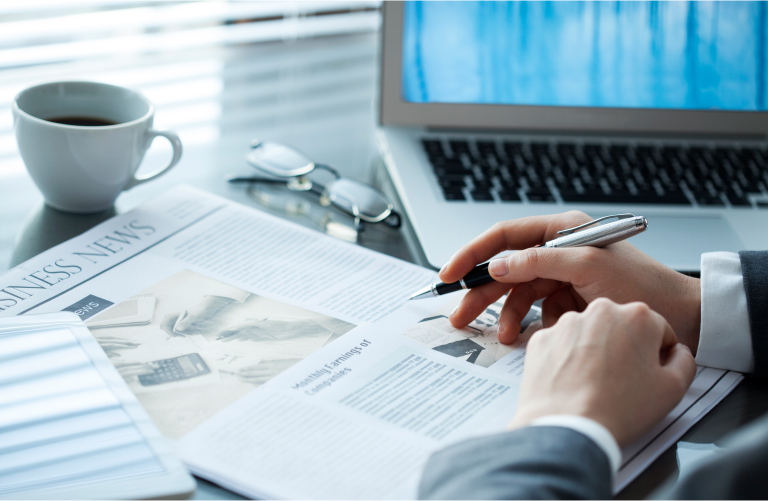
We recommend the new H6S intelligent thermal camera. It features the new ApexVision infrared imaging system, offering comprehensive upgrades in image clarity, temperature measurement accuracy, and the ability to identify the thermal features of minute targets.
When paired with a dedicated macro lens, the H6S can achieve a spatial resolution of 37.8μm at a close distance of 50mm . With a magnification of 3×, it can clearly distinguish the fine structures on microchips and precision optical modules, and capture the temperature field and heat distribution of key parts such as circuit traces and solder joints in real time, leaving no potential "thermal hazards" undetected , and providing strong support for high-precision R&D and quality control .
Guide Sensmart will continue to delve into ApexVision's cutting-edge technology, respond to the core challenges in the field of precision manufacturing, and help customers use more accurate and reliable thermal data to drive products to continuously break through the peak of high performance and high reliability.
















.svg)
.svg)



.jpg)