Thermal Imager Monocular: See in the Dark with One Eye Open

Imagine being able to see in the dark, without using a flashlight or any other type of light. With a thermal imager monocular, you can do just that. This device uses infrared radiation to create an image of objects even in complete darkness.
Not only is this incredibly useful for military and law enforcement purposes, but it can also be a lifesaver for civilians during emergencies.
However, there are a few things to keep in mind before purchasing a monocular. In this guide, we'll go over everything you need to know about thermal imager monocular so that you can make an informed decision.
What is a Thermal Imager Monocular?
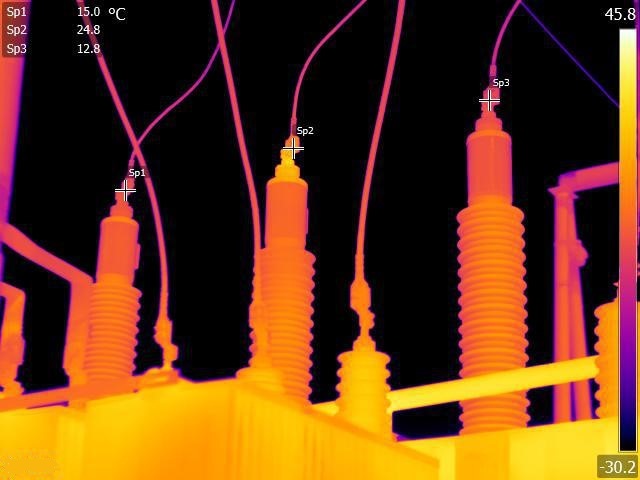
A thermal imager monocular is a handheld infrared camera that produces images of heat signatures. It uses an uncooled microbolometer to detect infrared radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. This signal is then processed to create a thermal image.
Thermal imagers are incredibly sensitive and can detect minute temperature differences. As a result, they can see through smoke, fog, and other obscurants that would otherwise block vision.
How Does a Thermal Imager Work?
All objects emit infrared radiation, also known as thermal radiation. This is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength that is longer than visible light but shorter than microwaves. The amount of thermal radiation emitted by an object depends on its temperature.
Hotter objects emit more thermal radiation than cooler objects. A thermal imager is able to detect this difference and create an image based on the intensity of the infrared radiation. The warmer an object is, the brighter it will appear in the image.
What are the Different Types of Thermal Imagers?
There are four main types of thermal imagers- nSb, HgCdTe, InGaAs, and QWIP FPA.
nSb detectors are made of cadmium mercury telluride (CMT), which is a compound semiconductor. They are the most common type of detector used in thermal imagers and have a high degree of sensitivity.
HgCdTe detectors are also made of CMT but with different stoichiometry. They are less common than nSb detectors but are more sensitive to changes in temperature.
InGaAs detectors are made of indium gallium arsenide (III-V), which is a direct bandgap semiconductor. They have a higher resolution than nSb and HgCdTe detectors but are less sensitive to changes in temperature.
QWIP FPA detectors are made of quantum wells, which are layers of semiconductor material with a well of electrons. They have a high degree of sensitivity and can operate at very low temperatures.
What are the Benefits of Using a Thermal Imager?
There are many benefits to using a thermal imager, especially during search and rescue operations, law enforcement activities, and military missions.
Some of the most notable benefits include:
• Enhanced Vision in Low-Light Conditions: Thermal imagers can be used to see in complete darkness. This is because they do not rely on visible light to create an image.
• Increased situational awareness: Thermal imagers provide a clear picture of the environment, even in obscured conditions. This allows you to see potential threats that might otherwise be hidden.
• Long-Range Detection: Since thermal imagers can detect minute temperature differences, they can be used to see objects at a great distance. And, because they don't rely on visible light, they can be used day or night.
• Versatile applications: With the help of additional accessories, such as night vision goggles, thermal imagers can be used for a variety of purposes, including navigation, target acquisition, and surveillance.
What to Look for When Buying a Thermal Imager

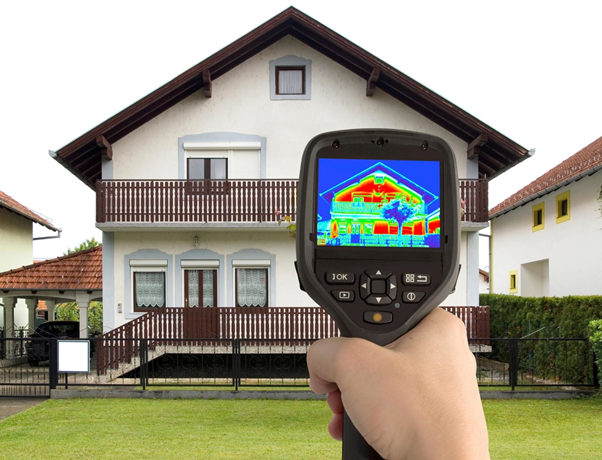
Now that you know the basics of thermal imagers, it's time to learn what to look for when purchasing one.
Here are a few things to keep in mind:
1. Resolution
Your thermal imager's resolution will determine how much detail you can see. The higher the resolution, the better. For instance, a 320x240 thermal imager will have 76,800 pixels, while a 640x480 imager will have307,200 pixels.
Furthermore, some manufacturers measure resolution in terms of NETD (Noise Equivalent Temperature Difference). This is the minimum temperature difference between two objects that your imager can detect. A lower NETD means better resolution.
2. Field of View
Your thermal imager's field of view (FOV) will determine how much area you can see at once. A wider FOV means you can see more, while a narrower FOV means you can see less. Usually, FOV is expressed in degrees. For example, a 30° FOV means you can see an area that's 30° wide.
3. Thermal Sensitivity (NETD)
As we mentioned before, NETD is a measure of your thermal imager's resolution. The lower the NETD, the better. A good rule of thumb is to look for an imager with a NETD of 0.1°C or less.
4. Refresh Rate
Your thermal imager's refresh rate determines how often it updates the image. A higher refresh rate means a more responsive image, while a lower refresh rate means a less responsive image. Usually, thermal imagers have a refresh rate of 9 Hz or 30 Hz.
5. Image Storage
Some thermal imagers can store images and video, while others can only store images. If you think you might want to store your images and videos, make sure to get a thermal imager with that capability.
6. Battery Life
Your thermal imager's battery life will determine how long you can use it before having to recharge or replace the batteries. Typically, thermal imagers have a battery life of 4-8 hours.
7. Weight and Size
Your thermal imager's weight and size will determine how easy it is to carry and use. If you plan on using your imager for long periods of time, make sure to get one that's comfortable to hold and use.
8. Warranty
Most thermal imagers come with a 2-year warranty. However, some manufacturers offer extended warranties for an additional cost. If you think you might need an extended warranty, make sure to get one from a reputable manufacturer.
Consider all of these factors before making your purchase, and you'll be sure to get the best thermal imager for your needs.
Final Thoughts
Thermal imagers are an incredibly useful tool for a variety of applications. Whether you're using it for navigation, target acquisition, or surveillance, a good thermal imager can give you the edge you need. Just remember to keep the resolution, the field of view, thermal sensitivity, refresh rate, image storage, battery life, weight and size, and warranty in mind when making your purchase.
Looking to Buy a Thermal Imager?
If you're in the market for a thermal imager, check out Sensmart's selection of high-quality thermal imagers. With resolutions of up to 640x480, thermal imagers from Sensmart provide clear images, even in low-light conditions. And, with a refresh rate of 30 Hz, you'll never have to miss a thing.













.svg)

.jpg)
.jpg)