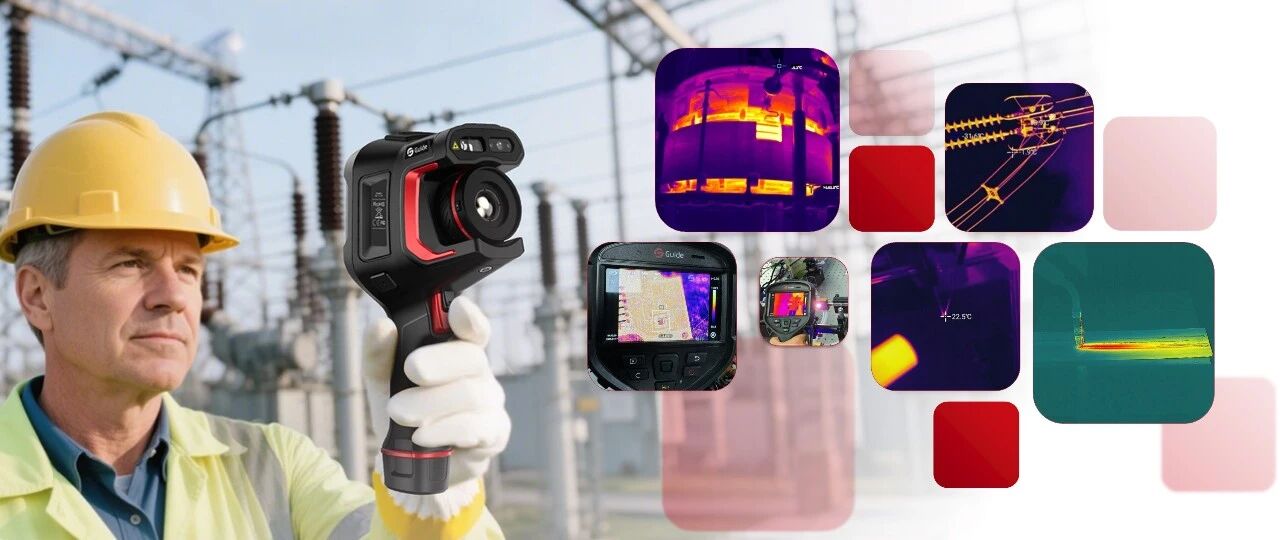
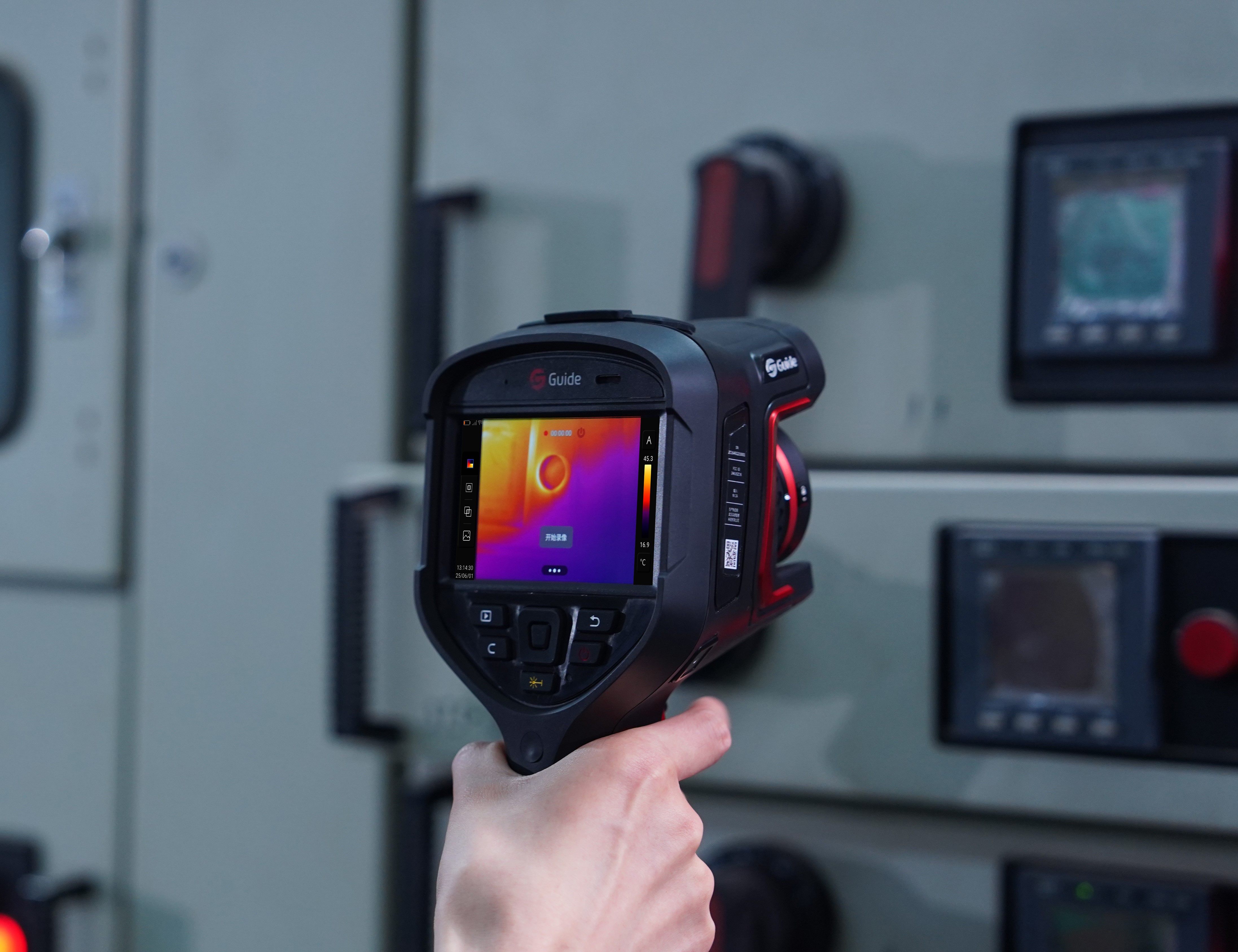
In modern factories, ensuring smooth machine operation and consistent product quality is essential. Industrial thermal cameras are now a core tool enabling non-contact detection of heat distribution patterns. They not only detect problems, but also prevent them before they occur. From predicting when a machine may fail to checking if a product meets standard, these thermal imaging cameras play a key role in promoting equipment maintenance and quality control. Let's discover how they connect these two important areas.
Predictive Maintenance: Stop Failure Before it Happens
Early Warning for Moving Parts
Machines with motors, bearings or gears often fail due to overheating of the components. During routine inspections, industrial thermal cameras can spot bearings that are 10°C hotter than normal. This early rise in temperature is a first sign of wear. By attending to it promptly, a factory can avoid unplanned shutdown. For example, a conveyor system motor pulley that is overheating and detected by a thermal imaging camera can be replaced during a planned shutdown rather than causing a costly production stoppage. Even in high-speed equipment such as textile looms, thermal imaging cameras can identify overheated yarn guides. Early detection of these problems can prevent thread breaks and production delays.
Monitoring Electrical Systems
Electrical panels, wiring, and transformers are prone to overheating when connections become loose. Thermal imaging cameras can quickly scan these areas, revealing hot spots that indicate increased resistance. This allows electricians to tighten connections or replace components before a fire breaks out. Unlike traditional inspections that require power outages, thermal imaging cameras work while the system is running, ensuring production is not impacted. In large plants with hundreds of electrical cabinets, automated thermal scanning systems can even send real-time alerts to maintenance teams via mobile apps.
Tracking Cooling System Issues
Equipment such as hydraulic presses and injection molding machines rely on cooling systems. If the cooling lines are blocked, the machine will heat up. Thermal imagers can detect temperature spikes on these systems, even behind metal housings. For example, when the cooling pipes of a plastic molding machine are blocked, hot spots will appear on its surface. Unblocking the pipes in time can avoid mold damage and product defects.
Quality Control: Ensuring Products Meet Standards
Detecting Hidden Defects in Manufacturing
During the production process, industrial thermal cameras can check whether the product is up to standard. In metal casting, for example, thermal imaging cameras can identify uneven cooling of parts, which often means that there are internal cracks or weak spots that cannot be seen by the naked eye. Within the electronics industry, it can check whether solder joints on the circuit board are heated properly. Cold solder joints have low strength and will lead to premature product failure. For smartphone screens, thermal imaging is employed to detect whether the backlight is evenly distributed to avoid visible dark spots in the finished product.
Verifying Heat Treatment Results
Many metal parts require heat treatment to increase their strength. Industrial thermal cameras can verify that heat is evenly applied: a gear with insufficient heat in one area will be more fragile and wear more quickly. By scanning parts after treatment, factories can determine that every product meets hardness standards, reducing returns and recalls. This is important in aerospace production, particularly for components such as turbine blades where even a 5°C temperature difference during heat treatment can affect their ability to withstand high pressures.
Checking Seals and Insulation Performance
In packaging, thermal imaging cameras can confirm that food or pharmaceutical containers are sealed tightly. Cool spots along the seal indicate leakage points, which can lead to spoilage. For insulated products such as refrigerators and pipes, they can detect heat leaks, which are identifying areas of missing or insufficient insulation, reducing the energy efficiency of the product. In the building industry, they can even check internal insulation before installing wall panels to check if that buildings meet energy-saving standards.
Advantages of Industrial Thermal Cameras
These cameras are fast, capable of scanning an entire machine or product in seconds. They don't require contact with surfaces, so they won't damage delicate items or disrupt production. They also record thermal measurements, allowing for long-term comparison of measurement results. For example, a factory can track the temperature trend of a motor over six months and create a customized normal range for it. This consistency helps factories establish clear standards for equipment health and product quality.
Choose Guide Sensmart's Industrial Thermal Camera Solutions
Our industrial thermal imaging cameras stand out with intelligent features that adapt to complex factory scenarios. Equipped with AI-powered analysis algorithms, they automatically distinguish between normal temperature fluctuations and abnormal heat sources, such as ignoring temporary temperature increases at motor startup and focusing on persistent overheating that indicates a fault. This reduces false alarms and enables more targeted maintenance.
Industrial thermal cameras are more than just tools; they connect predictive maintenance and quality control. By detecting overheating components early, they keep machines running and avoid production delays. During quality inspections, they can detect hidden defects that could lead to product scrap. Thermal imaging cameras are essential for factories looking to reduce costs, improve safety, and produce reliable products. As manufacturing continues to advance, their role in ensuring production efficiency and product quality will only grow in importance. Contact Guide Sensmart for more information about thermal imaging cameras.
















.svg)
.svg)