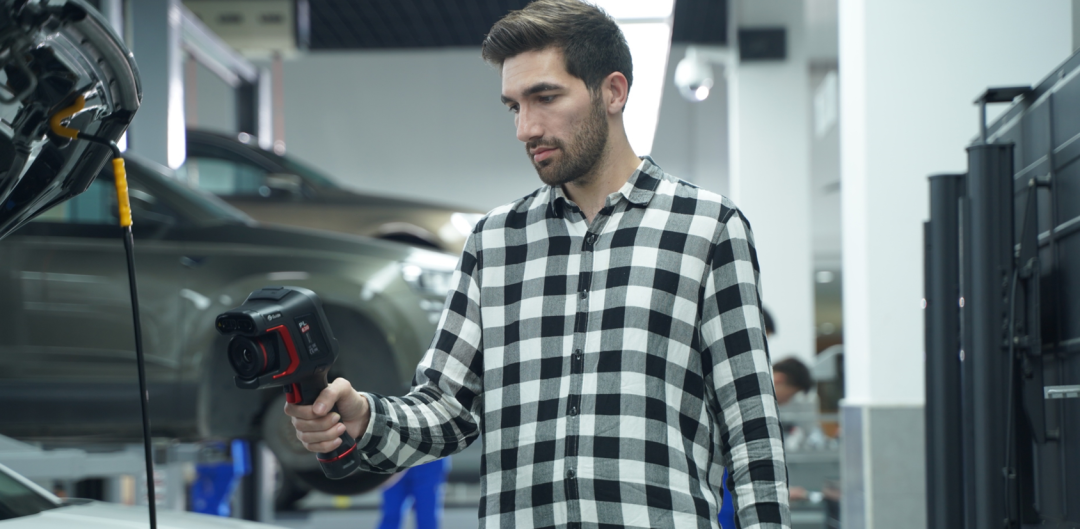
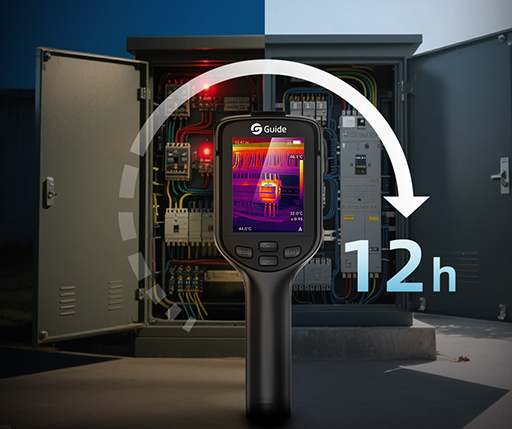
Safety and reliability are paramount in modern industrial power systems. Power plants, factories, and substations depend upon an uninterrupted and consistent supply of power to continue their operations. However, electrical systems possess the subtle risk of equipment overheating, loose wires, or blown insulation. Thermal imaging bridges this gap. Using advanced devices like an infrared thermal imager or thermal camera, engineers and maintenance staff can gauge hidden heat patterns that outline defects before they become failures.
The Requirement for Early Detection in Power Systems
Electrical failures are not necessarily discernible to the human eye. A cable might appear okay when, in fact, it is degrading internally due to overcurrent or physical stress. With the passage of time, minor faults can lead to arc flashes, fires, or even a complete system shutdown. Standard inspection practices, such as manual inspection or basic electrical testing, may not be able to identify tiny but perilous issues.
Thermal imaging offers maintenance engineers the ability to see heat patterns in real time. There is always a heat signature emitted by all electrical equipment, circuit breakers, and transformers whenever in operation. At first, unusual temperature variations are the warning signs for problems like loose connections, overloads, or breakdown of insulation. It is better to detect such anomalies in advance than later, so that action is taken before the chance of catastrophic breakdowns.
How Infrared Thermal Cameras Can Be Used to Supplement Inspections
The most popular tool for power system diagnostics during the past decade is the infrared thermal camera. Whereas regular cameras detect visible light, these cameras trace infrared radiation from objects. Since all the components of a power system generate heat, an infrared thermal camera can convert invisible energy into a distinct color-coded thermal image.
This allows inspectors to detect overheated wires, faulty switchgear, or blown fuses without stopping operations. For instance, the busbar connection may appear normal to the eye but register as a white hotspot with thermal imaging, pointing towards a potentially severe condition. Facilities avoid risking equipment malfunction and unplanned downtime by fixing the issue on time.
Another advantage of infrared thermal cameras is that they are non-contact. Inspectors can sweep from a safe distance with less exposure to high-voltage environments. This makes the application of thermal imaging not just efficient but safer to employ in industrial use as a diagnostic technique.
The Use of Thermal Camera Imagers in Predictive Maintenance
Though infrared cameras are firmly established, a thermal camera imager provides greater capability for application in continuous monitoring and predictive maintenance. Unlike handheld devices used in conventional periodic inspection, thermal camera imagers can be permanently mounted at substations, switch rooms, or control centers.
Such systems will track and record temperature automatically and alert in case of abnormal heat patterns. For example, where there is a transformer winding overloaded and overheating because of overload above capacity, the thermal camera imager can instantly alert the operators. This provides time for prompt intervention before the condition deteriorates.
Proactive equipment maintenance with thermal imaging technology optimizes equipment life, conserves maintenance cost, and hugely improves overall system reliability. Companies can move away from reactive repairs after failures occur and instead take proactive measures based on real-time thermal data.
Advantages Beyond Fault Detection
The advantages of power systems thermal inspection in industry go beyond fault detection. Some of the most important advantages are:
Enhanced Safety: Workers are protected against hazardous equipment failure through fault identification at the earliest possible time.
Continuity of Operations: Testing can be undertaken without removing equipment from service, thereby ensuring continuity of operations.
Cost Reduction: Prevention of unplanned outages translates into loss reduction of downtime and repair costs.
Regulatory Compliance: Many safety codes encourage or mandate the use of thermal inspections on critical power equipment.
Thorough Documentation: Thermal camera imagers and infrared thermal cameras provide concrete proof in the form of a report, which can be used for auditing, training, and continuous monitoring of a system.
Future of Thermal Imaging in Industrial Applications
Thermal imaging grows increasingly accurate and affordable with technological advancements. Small infrared thermal cameras are presently employed in combination with drones to enable top-quality transmission line inspections, while AI-powered thermal camera imagers can automatically scan patterns and make failure predictions with precision. All these advances ensure that thermal imaging remains the cornerstone of industrial power system reliability.
Conclusion
In an era when industrial processes demand optimal uptime and safety, thermal imaging has been the spoiler. With instruments such as the infrared thermal camera and thermal camera imager, industries are capable of detecting hidden electrical faults before they lead to life-critical accidents. Early fault detection, preventive maintenance, and enhanced worker safety all result in improved power systems.
In summary, thermal imaging is not merely a diagnostic tool but also an active protective measure that safeguards both equipment and human lives. For any structure that has intricate electrical installations, employing this technology is no longer a choice but something that is mandatory.
















.svg)
.svg)