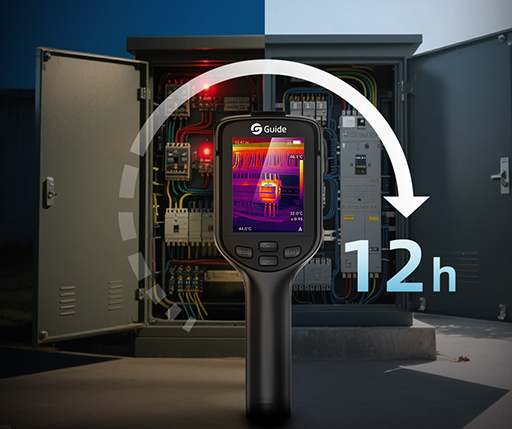
Early detection is the most powerful defense against catastrophic fires in modern safety management. Whereas the conventional smoke detectors react in the instance of flames or smoke, today's advanced imaging technologies take a more proactive approach by identifying danger long before ignition. Fire prevention cameras are fast becoming indispensable tools for industry, emergency response teams, and facility managers alike. This is because their ability to detect heat anomalies, electrical faults, and hidden hotspots forms an indispensable part of any comprehensive fire prevention strategy.
Why Early Heat Detection Matters
Most large fires start off small, often caused by cable overheating, friction within mechanical equipment, or chemical reactions inside storage areas. These incipient signs of a fire are not even visible to the naked human eye, hence difficult to recognize unless appropriate tools are available. A good-quality fire prevention camera can identify temperature changes and abnormal heat signatures in real time to allow safety personnel to take action long before visible fire develops. This shift in approach toward proactive monitoring rather than reactive helps reduce property loss, decreases downtime, and lessens safety risks for workers and communities around the area.
How Thermal Imaging Technology Works
Infrared thermal imaging is the very heart of these devices. That means everything emits infrared radiation due to its temperature. Thermal cameras detect that radiation and convert it into digital images that highlight areas of concern. A fire-service thermal imaging camera can depict heat patterns behind walls, inside machinery, or even in places hard to reach but where conventional sensors may fall short.
A firefighting thermal imaging camera is specifically designed to enhance visibility in no-visibility conditions. Thick smoke, darkness, and debris at emergency scenes can blind a firefighter's eye. Thermal imaging cuts through all these obstacles to help responders find victims, move around in structures more quickly, and locate hotspots.
Key Features of Modern Fire Prevention Cameras
Today, fire prevention camera systems have various functions that provide improved early detection capabilities:
1. Real-time heat monitoring
Continuous temperature measurement means that teams can identify abnormal heat levels instantly. This becomes particularly useful in electrical rooms, battery storage stations, and other manufacturing areas where overheating often occurs.
2. AI-Enhanced Risk Identification
Some modern cameras incorporate AI algorithms that interpret thermal patterns to highlight dangerous conditions automatically. For example, such a camera might identify unusual patterns in machinery heating as conditions predictive of mechanical failure and let operators know to schedule preventive maintenance.
3. Capabilities for Remote Surveillance
The most typical fire service thermal imaging camera used in emergency departments is handheld; however, an industrial fire prevention system is normally integrated into centralized monitoring networks. Remote access enables safety management teams to monitor several facilities all at once and respond promptly to alerts.
4. High Sensitivity and Wide Detection Range
The primary difference between a firefighting thermal image camera and the ordinary tools is their ability to detect even minute temperature differences. High-resolution sensors, coupled with wide scanning angles, help in covering big areas with precision.
Applications Across Industries
Different environments bring different fire hazards, and thermal imaging technology adapts to each scenario.
Industrial plants
Factories that utilize heavy machinery run the risk of overheating motors, friction on conveyor belts, and exothermic chemical reactions. The fire prevention camera constantly scans for any anomaly in temperature. This enables preventive maintenance that can avoid costly operational shutdowns.
Power Stations and Electrical Facilities
Thermal imaging is very helpful in the evaluation of loose connections, overloaded circuits, and defective transformers. A technician can safely evaluate electrical components with a fire service thermal imaging camera from a distance without contact.
Warehouses and Logistics Centers
Such facilities often store flammables. Early detection by a thermal image camera used for firefighting helps in establishing hotspots created by battery packs, packaging friction, or poorly ventilated storage zones.
Public Buildings and Commercial Spaces
It can also monitor HVAC, electrical panels, and utility rooms with thermal cameras. Integrating fire-prevention thermal imaging into the overall building management systems enhances safety and reduces downtime.
The Role of Thermal Cameras in Emergency Response
Firefighters rely heavily on visibility and situational awareness in times of crisis. In firefighting, a fire service thermal imaging camera helps the rescue team to locate victims behind smoke, identify structural weaknesses, and extinguish hotspots that may lead to re-ignition. These handheld devices are rugged, easy to handle, and calibrated to withstand the extreme firefighting environment.
On the other hand, fixed-mount thermal monitoring systems provide continuous surveillance, alerting teams before a fire ever starts. Combining these two types of equipment will form a complete defense strategy: prevention and emergency response.
Conclusion: A Smarter Approach to Fire Safety
Through the process of evolution, thermal imaging has revolutionized the way organizations manage fire risks, supported by the operation of emergency teams. These can start with a fire prevention camera, a fire service thermal imaging camera, and a thermal image camera for firefighting; these enable the organization to uncover hidden threats, reduce equipment failure, and rapidly respond in case of emergencies.
As demands for safety continue to rise, investment in early detection technology is no longer optional but compulsory. With thermal imaging, teams can take proper precautions before the disaster strikes and save human lives, assets, and the long-term viability of operations.
















.svg)
.svg)