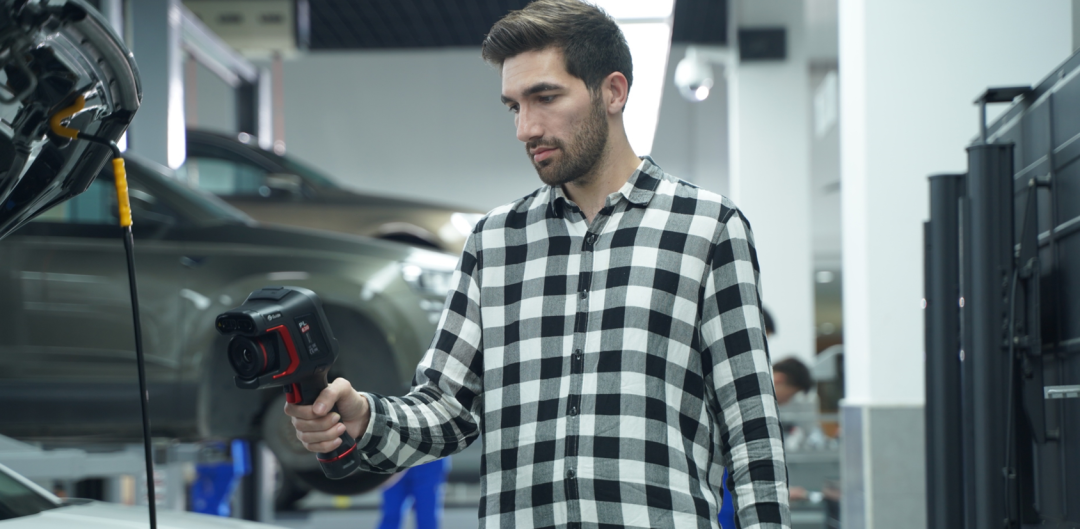
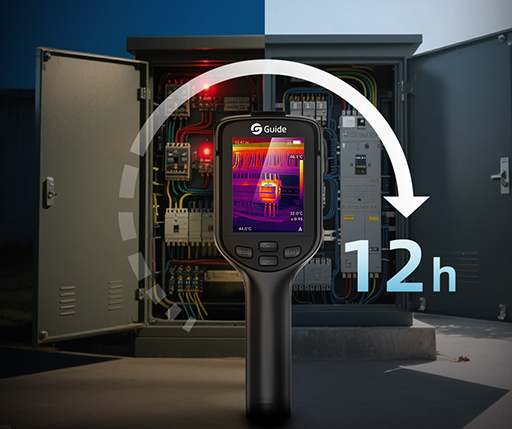
Smooth operation of machinery is vital in maintaining productivity and profitability in the complex of the contemporary industry. Industrial thermal imaging cameras now represent a technologically advanced tool for accurately determining complex equipment and preventing potential malfunctions.
Understanding Thermal Imaging
Thermal imagers function by detecting infrared radiation from objects. Every object above the temperature of absolute zero gives off infrared energy. The radiation is different with different changes in object temperature. Thermal imagers transfer infrared radiation to a viewable image within the visible spectrum where temperatures range differently corresponding to shades of color. This heat pattern image can be beneficial in assessing the working status of mechanical devices.
Diagnosing Mechanical Issues
Bearing and Gear Failures
Gears and bearings are critical components of rotating equipment such as motors and industrial gearboxes. Over time, overheating can be caused by wear, misalignment, or a lack of lubrication. Resultant heat pick-up is easily trapped with industrial thermal imaging cameras. A worn bearing, for example, would exhibit noticeable hot spots as a result of overheating due to friction. Through occasional scanning of these parts using an industrial thermal imaging camera, maintenance engineers can spot the onset of wear and schedule prompt repair to prevent disastrous failure.
Belt and Pulley Problems
Belt and pulleys are the most common source of power transmission in industrial machinery. Pulley misalignment or belt slippage can cause excessive heat creation. Thermal imager cameras quickly identify hotspots, which might indicate problems. Maintenance staff would then adjust the belt tension or align pulleys before belts and pulleys initiate extensive damage or affect the process of production.
Electrical Fault Detection
Overheating of Electric Connections
Electrical connections in equipment, such as in circuit breakers and switchgear, will work loose over time. Loose connections lead to increased resistance, and resistance creates heat. Industrial thermal cameras can detect these overheated connections, even in areas that are difficult to access. This is significant because overheated electrical connections will not only damage equipment, but can also lead to fires.
Insulation Failure
Insulation failure in electrical components can cause the accumulation of heat. Unusual temperature patterns in insulated wires, transformers, and other electrical components can be recorded using industrial thermal cameras. Detection at an early stage can enable businesses to avoid electrical shorts and component failure, hence making electrical systems safe and trustworthy to operate.
Diagnostic Process
Regular Inspections
In order to effectively diagnose complicated equipment, regular thermal imaging examination is required. The maintenance staff should develop an organized inspection pattern based on equipment severity and method of operation. For high-hazard or heavy-use equipment, daily or weekly examination can be done, while for less critical equipment, examination done monthly or quarterly can suffice.
Data Analysis
After the thermal images are captured, the information has to be analyzed. This involves comparing every component's temperatures to their usual operating parameters. Higher-grade thermal imaging cameras often come with software capable of automatic analysis, indicating areas of faults. Maintenance technicians then use this to determine the severity of the fault and formulate proper remedial action.
Follow-up Actions
From the analysis results, the maintenance team can take action promptly. Minor issues, such as belt tensioning or tightening electrical connections, can be repaired in the field. For more serious issues, such as extensively worn bearings, a detailed repair or replacement strategy can be devised. Routine follow-up inspections must also be done to ensure that corrective actions have completely resolved the issue.
Advantages Compared to Traditional Diagnostic Techniques
Non-contact safety inspection: Without physical contact to high-risk or high-voltage equipment, inspections could be conducted.
Quick and efficient: Scanning large plants or complex machines can be achieved in minutes.
Cost optimization: Reduce downtime and extend equipment lifespan through early fault detection.
Quantitative analysis: Develop thermal reports to enable compliance audits and performance measurement.
Conclusion
In conclusion, industrial thermal imaging cameras are an investment worth considering in the industrial field. Industrial thermal imaging cameras present a non-intrusive, fast and accurate method of troubleshooting complex equipment. By detecting potential problems early, industries can cut down on costs associated with unexpected shutdowns, repairs, and replacement of equipment. At Guide Sensmart, we are committed to providing quality thermal imaging solutions. We design our products with the latest technology to meet different industries' differing needs. Contact us now!
















.svg)
.svg)