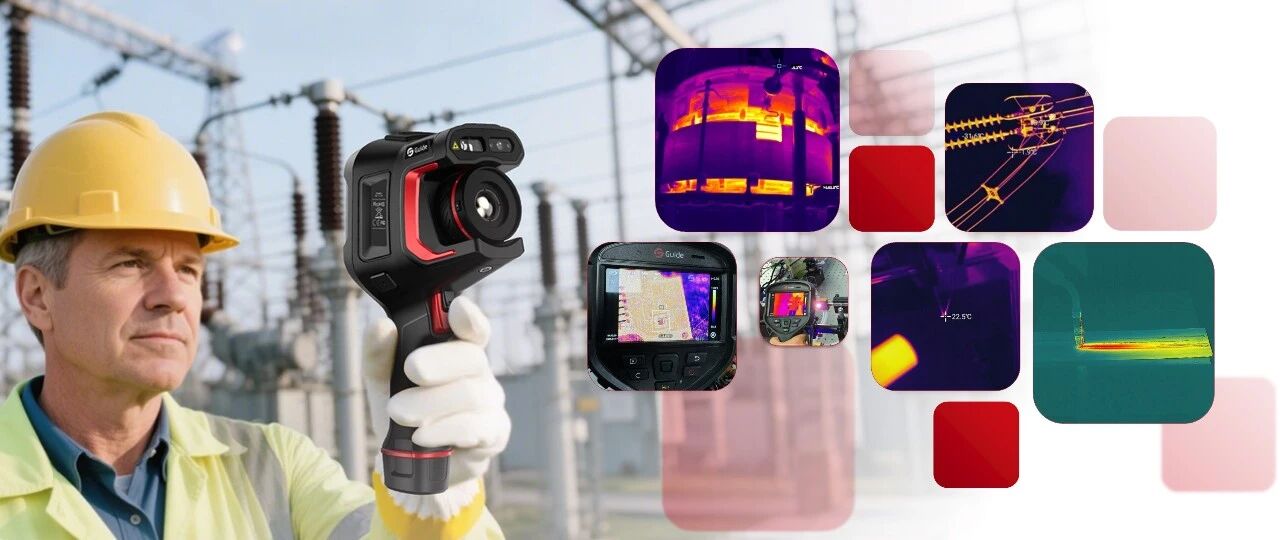
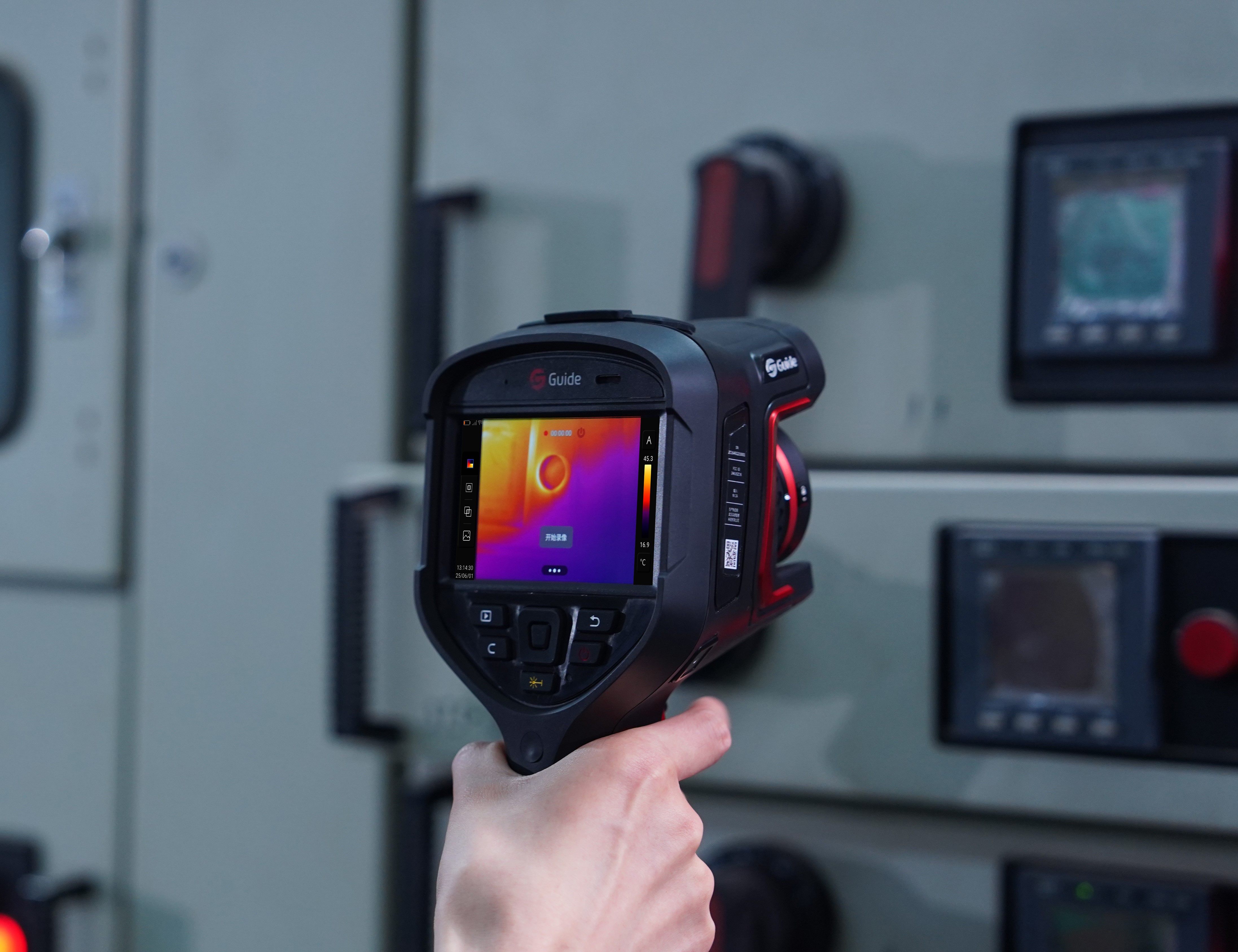
Equipment reliability and energy efficiency are indispensable in industrial operations. Heat loss is an everyday but often neglected problem that can generate colossal amounts of lost energy, increased operating costs, and even pose safety hazards. Thermal imagers have emerged as the indispensable tool in heat loss detection and analysis for companies, allowing companies to streamline process, conserve energy, and prevent costly equipment failures. This is an article that explains the main applications of thermal imaging cameras in the detection of industrial heat loss and their implications on existing manufacturing and engineering industries.
Understanding the Importance of Heat Loss Detection
Heat loss is where heat energy is dissipated from industrial processes such as pipes, furnaces, boilers and tanks. In the majority of industries such as power generation, chemical processing and manufacturing, the majority of input energy is lost due to improper equipment operation, seal failure or poor insulation. Preparation for early identification of heat loss issues not only ensures compliance with environmental codes by companies, but also increases economic benefit via energy cost savings and extended equipment lifespan.
Thermal Camera Imagers: the Precise Tool for Heat Loss Detection
Thermal imagers work by capturing infrared radiation emitted by objects and converting it into a visual image in which shades of color represent shades of temperature. The contact-free, intrusion-free process allows for quick scanning of large areas to identify hot and cold spots that may indicate heat loss or insulation failure. With capabilities such as high-resolution imaging, adjustable sensitivity and real-time data analysis, thermal camera imagers provide accurate and complete information on the thermal status of industrial equipment.
Key Applications in Industrial Sectors
Power Generation
In power plants, thermal imaging cameras are employed to monitor the efficiency of boilers, turbines, and electrical systems. In boilers, the cameras will be able to show hotspots on the outer surface, which can be due to degraded insulation or an imbalanced heat distribution. It can prevent heat loss, reduce fuel consumption, and prevent boiler explosion if the issues are detected early. In electrical distribution systems, infrared imaging identifies overheating transformers, switchgear, and power lines, allowing proactive maintenance to avoid power disruptions and electrical fires.
Chemical Processing
Chemical Industry employs high-temperature reactors, distillation columns, and pipelines. Loss of heat in such units can not only lose energy but also degrade the quality of chemical products. Thermal imaging cameras monitor the insulation of the reactors' and pipes' to maintain reaction temperatures within set limits. These can also detect leaks in flanges and valves, which result in loss of heat and danger to safety as a result of release of harmful chemicals.
Manufacturing
Heat loss can occur in manufacturing factories during processes such as forging, heat treatment, and metal casting. Thermal camera imagers measure temperature in furnaces, cooling systems, and molds. Manufacturers can achieve production process improvement, product quality, and scrap reduction by viewing temperature gradients. For example, in metal casting, uneven heating can cause casting defects. Thermal cameras enable operators to monitor and regulate temperature changes in real-time, enabling uniform product quality.
Oil and Gas
Thermal imaging cameras in the oil and gas industry have been given a noteworthy place to utilize in pipeline, tank, and offshore platform inspection. Heat loss in pipes results in increased energy expenditure to maintain fluids at a temperature and may also cause corrosion and condensation. Thermal imaging cameras detect damage to insulation damage, leaks, and abnormal temperature gradients along the pipelines such that repairs can be undertaken early and environmental disasters prevented. For storage tanks, the cameras can identify hotspots that may be a sign of internal corrosion or product degradation on the inside.
Benefits of Using Thermal Imaging Cameras for Heat Loss Detection
Early Fault Detection
Infrared thermal cameras also detect heat loss and potential equipment failure prior to the symptom being apparent, thus companies can perform proactive maintenance, reduce the likelihood of unplanned failures, and reduce downtime in production.
Energy Efficiency
By identifying and addressing the areas of heat loss, businesses can greatly reduce their energy consumption. Minor improvements in equipment efficiency or insulation can, over time, conserve a significant amount of energy expenses.
Safety Enhancement
Heat loss can sometimes signal safety hazards, such as electrical fires or chemical leaks. Infrared thermal cameras are employed to detect such hazards beforehand, and businesses can take precautionary measures to ensure a safe working environment.
Conclusion
In summary, thermal imaging cameras have forever altered industrial heat loss detection, providing an energy-saving solution to improve energy efficiency, equipment reliability and safety. If you have any interest in thermal imaging cameras, please do not hesitate to contact us.
















.svg)
.svg)